|
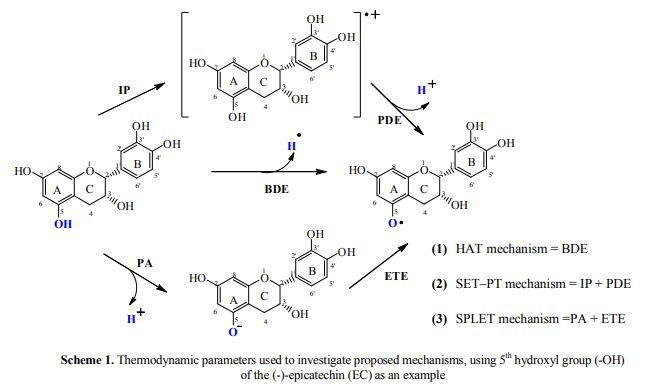
In this computational investigation, antioxidant potentials of the four major catechins [(-)- epicatechin (EC), (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)- epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), and (-)-epigallocatechin-3- gallate (EGCG)] present in green tea were explored from the thermodynamic point of view. HAT, SET–PT, and SPLET mechanisms were used to illustrate their radical scavenging activities in the aqueous phase using solvation models. It was revealed that the HAT mechanism has demonstrated the lowest set of enthalpies compared to other two reaction mechanisms (SET-PT and SPLET). It was positively obvious that (-)-epigallocatechin-3- gallate (EGCG) possessed the lowest set of average enthalpies as showing the highest antioxidant potential as compared to the other three catechins. Based on average enthalpies, antioxidant potential of catechins found in green tea can be placed in the following order of ascending: EC < EGC < ECG < EGCG. It can be concluded that modification of the chemical structure of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) provides an insight into the design of structurally novel, potent antioxidants which will be more economical and beneficial in pharmaceutical industry.
|
 |
|
|
Sanduni S. Wijesooriya, Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Chemistry & Chemical Technology |
||
Abstract:- https://doi.org/10.23939/chcht16.04.591
|
||

- 011 2903539 / 539
- officerc@kln.ac.lk
- Mon - Fri 8:00 - 17:00
Quick Links
Contact us
Research council
University of Kelaniya, Kelaniya 11600,
Sri Lanka
+094 (112) 903 539
officerc@kln.ac.lk
Latest News
Test
