|
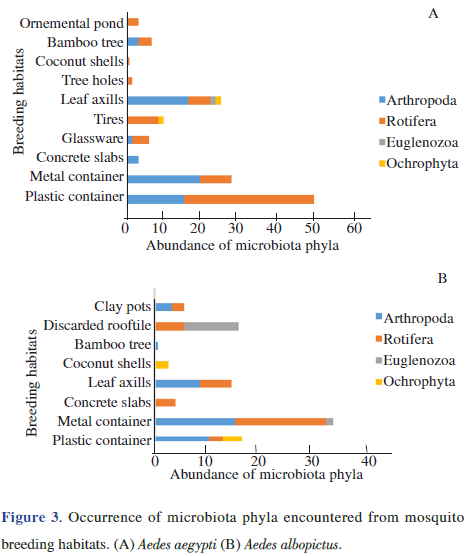
Identification of parasitic, epibiont, pathogenic, competitive or predatory microbiota in larval habitats and their interactions with associated mosquito larvae, in terms of controlling agents, would be beneficial for potential larval-controlling approaches. The degree of such parasitic, pathogenic, or predatory effects may vary with the geographical location. During the present study, a total of eleven and eight microbiota species were identified from Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus breeding habitats respectively from Udapalatha MOH division. The relative distribution of microbiota associated with mosquito species differed significantly among the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus revealing the relationship of microbiota abundance with different mosquito species which helps in implementing novel vector-control strategies in the study area in an ecofriendly manner. |
 |
|
|
J.Y. Kumari, L.D. Amarasinghe, H.A.K. Ranasinghe Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine |
||
Abstract:- https://doi.org/10.4103/1995-7645.380722 |
||

- 011 2903539 / 539
- officerc@kln.ac.lk
- Mon - Fri 8:00 - 17:00
Quick Links
Contact us
Research council
University of Kelaniya, Kelaniya 11600,
Sri Lanka
+094 (112) 903 539
officerc@kln.ac.lk
Latest News
Test
